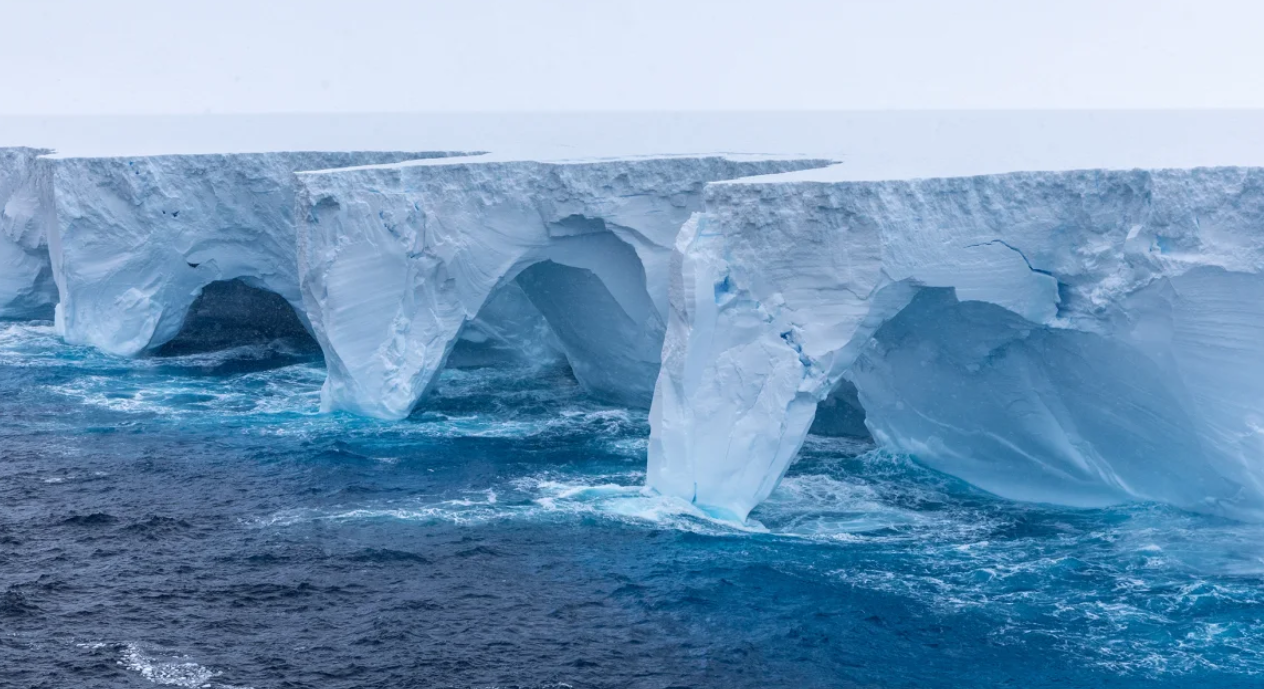
The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, is moving once again. Scientists at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) have said that the iceberg’s movement in the Southern Ocean had been halted for months.
When calculated in August 2024, the extension of the A23a was 3,672 sq. km (1,418 sq mi), which is slightly larger than Rhode Island in the US. This glacier separated from the Filchner- Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986. Scientists have been studying it ever since.
For more than 30 years, the iceberg has been stuck at the bottom of the Weddell Sea in Antarctica. As its size decreased over time, it became free from the bottom. The iceberg was then moved by ocean currents, but became trapped again in a swirling circle of water called a “Taylor column”. A Taylor column is a trough of water formed by currents striking mountains below the sea floor.
Now the iceberg is free again and according to scientists, it is riding the ocean currents and moving towards South Georgia Island. There it will break up into smaller pieces and then melt and disappear.
The A23a iceberg has held the title of “largest current iceberg” several times since the 1980s. However, the title has sometimes been usurped by larger but shorter- lived icebergs, such as A68 (2017) and A76 (2021).
Scientists say the A23a ice sheet has separated as part of a natural cycle and will not affect sea level rise. However, there are indications of severe effects of climate change on the Antarctic continent, which could lead to global sea level rise.
During the voyage to the iceberg, scientists studied its erosion and learned how sea ice affects global cycles of carbon and nutrients. Biogeochemist Laura Taylor at BAS said, “These huge icebergs pump nutrients into the sea and create rich ecosystems even in less productive areas.”
He added, “We don’t yet know exactly how specific icebergs, their size and origin, affect this process. We sampled the surface waters behind, near and in front of the icebergs. How this may have shaped the life around A23a and how it might affect the oceans.” It will help to understand how carbon and atmospheric balance are affected.”
Increasing impact of climate change:-
It is important to study how such natural phenomena affect ocean ecosystems and how it relates to global climate change. A23a’s journey is creating a unique opportunity for scientific research.